Apply the dialectic diagram to Barr’s. What would count as a thesis, an antithesis and a synthesis. You will need to refer to images of art works for a persuasive answer.
By studying Barr’s chart, it can be shown that at the beginning of the 20th Century Cubism acts as a thesis whilst Fauvism acts as an opposing antithesis. The emergence of Orphism can be seen as a synthesis of both of these two movements, being influenced by and using elements of both. To demonstrate this synthesis, the fundamentals of each movement will be discussed and art works indicated.
Cubism (Thesis)
Cubism was invented around the year 1907 by artists Pablo Picasso and Georges Braque. Analytical cubism gave way to synthetic cubism as the artists developed their ideas. Picasso and Braque developed a new form of realism that abandoned the traditional single point perspective form of representation. Instead they created a new form of realism to convey form and structure more accurately and convincingly. Inspired by Cezanne, who constructed forms out of different planes, Analytical Cubism used multiple viewpoints that created an experience of three dimensional objects in space and time. Movement is continuous as the viewer constructs, not just through sight but through thought as well, the suggestion of an object (Dempsey, 2002:85). Objects were reduced and fragmented to depict volume and mass in space.
Mandora (Fig 3.) illustrates the new perspective explored in analytical cubism. Overlapping planes, fragmented form and structure give the illusion of a more realistic depiction of subjects in space and time (Tate online s.d. Accessed 20/05/2020). It reflects our experience of life that flows through movement in time rather than exists in a static state.
In both Braque’s Mandora (Fig 3) and Picasso’s The Accordionist (Fig 4) the subject matter is similar. The two artists focused on neutral subject matter (still life) and completed their images in a subdued and monochromatic palette. This ensured that the whole of the viewers’ attention was focused upon the structure of the form and the density of the image.(Tate online s.d. accessed 20/05/2020)
In Synthetic Cubism (Fig 5), the artists started to flatten the image rather than breaking it down into multiple viewpoints. Experiments with collage, textures and patterns in their art helped to achieve this, alongside large blocks of colour (Dempsey, 2002:85).
Fuavism (Antithesis)
Fauvism was a movement that existed between 1905 and 1910 and included artists such as Henri Matisse and Andre Derain. After an exhibition at the salon d’automne in Paris, in 1905, the critic Louis Vauxcelles labelled this group of artists Les Fauves (wild beasts) due to their use of bold colours and wild brushstrokes . Unlike the cubists, who focused on realism of form, depth and structure through movement and time, the belief amongst this group of artists was that art should evoke emotional sensations through form and colour. The artists primarily expressed themselves through the use of bold, unnatural, strong colours which served to create atmosphere (Dempsey, 2002, 66).
Matisse’s Joy of Life (Fig 6) illustrates the Fauvist’s strong use of colour which creates a warm, inviting atmosphere. The curving simple lines create the forms of bodies reclining and relaxing amongst nature. The expression through colour and the simplified forms evokes sensations of pleasure and physical delight (Dempsey,2002:66). Similar to the cubists, the fauvists rejected traditional three-dimensional space and used flat areas of colour and spontaneous brushwork to flatten the surface of the canvas.
Scientific colour theory was important to the Fauvists and they paid particular interest in the 19th Century colour theories relating to the effects of complementary colours (Essaulova, s.d.). In Bridge to Charing Cross (Fig 7), Derain uses complementary colours to heighten the scene and allow the contrasting colours to heighten the impact of the painting.
Orphism (Synthesis)
The thesis (Analytical cubism) and the antithesis (Fauvism) act in opposition to one another. Cubism focuses on the structure of form and mass through time and space whereas Fauvism focuses on the expression of emotion through the use of colour and simple forms. Both movements reject the traditional forms of representation and flatten or give depth to the image. The synthesis for these two art movements is that of Orphism.
Orphism, that evolved from about 1912, included artists such as Frantisek Kupka, Robert Delauney and Sonia Delauney. These artists were highly influenced by the cubist and Fauvist movements taking elements from each. Fig 8. illustrates Delauney’s Red Tower which shows the representation of the subject matter from multiple viewpoints but also shows some Fauvist qualities by introducing a more striking subject matter and the use of bright bold colours.
As Orphism progressed, they started to move beyond reality into pure abstraction. There was a mystical and spiritual element to their paintings through the use of colour and shape. Like the Fauvists, colour theory became very important as they learnt the interrelationships of colour, light and movement and applied it to their work. Contrasting colours, colour harmonies and rhythms create expression that gives depth, form, movement and an emotional content (The art story, accessed 20/05/2020).
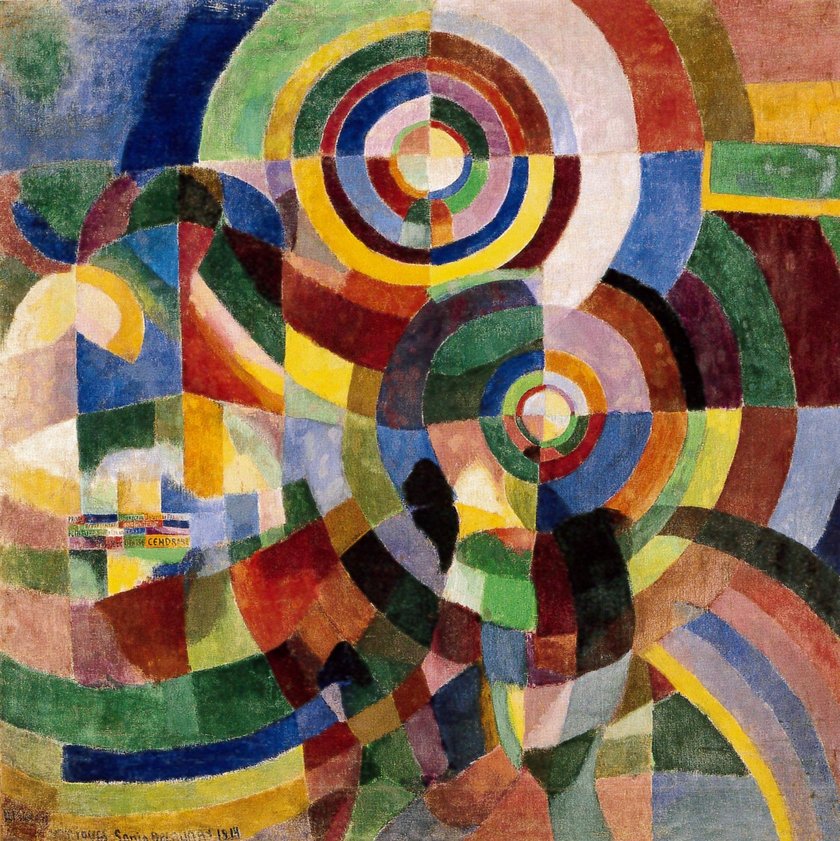
In the later stages of Orphism we can see a fusion of pure abstracted forms and an expressive interplay of colour (Fig 9. Prismes electriques) (Tate online, accessed 20/05/2020). The result is an expressive form of abstract art that draws attention to the flat surface of the canvas.
Orphism is a synthesis of Analytical cubism and Fauvism. Both movements rejected the traditional representation of three dimensional reality pushing them both towards near abstraction of form and a flattening of the image. The Orphists expressed themselves through bold bright colours based on colour theories of the time (Fauvism) and embraced the multiple fragmented viewpoints of cubism that ultimately led to pure abstraction.
Reflections
This was a very interesting exercise and it was fascinating to see how two movements could influence artists of the time. There seemed to be more opposing forces between Fauvism and Cubism than similarities, yet the two movements seemed to inspire the Orphists to create one of the earliest approaches to complete abstraction.
List of Illustrations
Fig 1. Diagram to illustrate Hegel’s dialectic of subjectivity and objectivity. At https://calmapossawi.tk/113-hegel-thesis-antithesis-synthesis-dialectic.php (Accessed 20/05/2020)
Fig 2. Barr, A.H. (1936) Cubism and Abstract Art. At https://www.moma.org/calendar/exhibitions/2748 (Accessed 20/05/2020)
Fig 3. Braque, G. (1909-10) Mandora [oil on canvas] At https://www.tate.org.uk/art/artworks/braque-mandora-t00833 (Accessed 20/05/2020)
Fig 4. Picasso, P. (1911) The Accordionist [oil on canvas] At https://www.guggenheim.org/artwork/3426 (Accessed 20/05/2020)
Fig 5. Gris, J. (1914) The Sunblind [oil on canvas] At https://www.tate.org.uk/art/art-terms/s/synthetic-cubism (Accessed 21/05/2020)
Fig 6. Matisse, H (1905) Joy of Life (Bonheur de Vivre) [oil on canvas] At https://www.henrimatisse.org/joy-of-life.jsp (Accessed 20/05/2020)
Fig 7. Derain, A. (1906) Bridge to Charing Cross [oil on canvas] At https://arthive.com/andrederain/works/323773~Bridge_To_Charing_Cross (Accessed 20/05/2020)
Fig 8. Delauney, R.(1912) The Red Tower [oil on canvas] At https://www.guggenheim.org/artwork/1020 (Accessed 20/05/2020)
Fig 9. Delauney, S. (1914)Prismes electriques [oil on canvas] At https://www.tate.org.uk/press/press-releases/ey-exhibition-sonia-delaunay (Accessed 20/05/2020)
Bibliography
Bois, Y-A (2004) with B.Buchloh, H. Foster, R. Krauss. Art since 1900 London and New York, Thames and Hudson.
Dempsey, A. (2002) Styles, Schools and Movements Thames and Hudson Ltd. London.
Esaulova, A. Bridge to Charing Cross At https://arthive.com/andrederain/works/323773~Bridge_To_Charing_Cross (Accessed 20/05/2020)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Orphism_(art) (Accessed 20/05/2020)
https://www.tate.org.uk/art/art-terms Accessed 20/05/2020
https://www.theartstory.org/movement/orphism/artworks/ (Accessed 20/05/2020)
https://www.metmuseum.org/toah/hd/fauv/hd_fauv.htm (Accessed 20/05/2020)











.jpg!Large.jpg)
.jpg!Large.jpg)